Since we all love to experiment, dig into system settings, run something of our own making, it is necessary to think about a safe place to experiment. Such a place for us will be a VirtualBox virtual machine with Windows 7 installed.
When starting the VirtualBox virtual machine (hereinafter referred to as VB), the user sees a window with a completely Russian-language interface.
Recall that when you install the application, the shortcut is automatically placed on the desktop. If this is your first time creating a virtual machine, you will find in this article that may be useful at this stage.
So, in a new window, click "Create", after which you can select the OS name and other attributes. You can choose from all available operating systems.
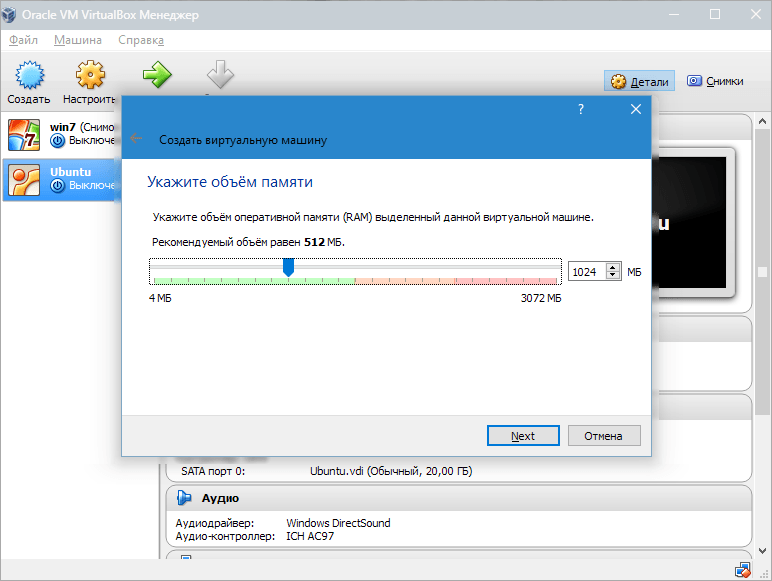
Go to the next step by clicking Next. Now you need to specify how much RAM to allocate to the VM. For its normal functioning, 512 MB is enough, but you can choose more.
After that, create a virtual hard disk. If you have previously created discs, you can use them. However, in the same article, we will focus on how they are created.
We mark the item "Create a new hard drive" and move on to the next steps.
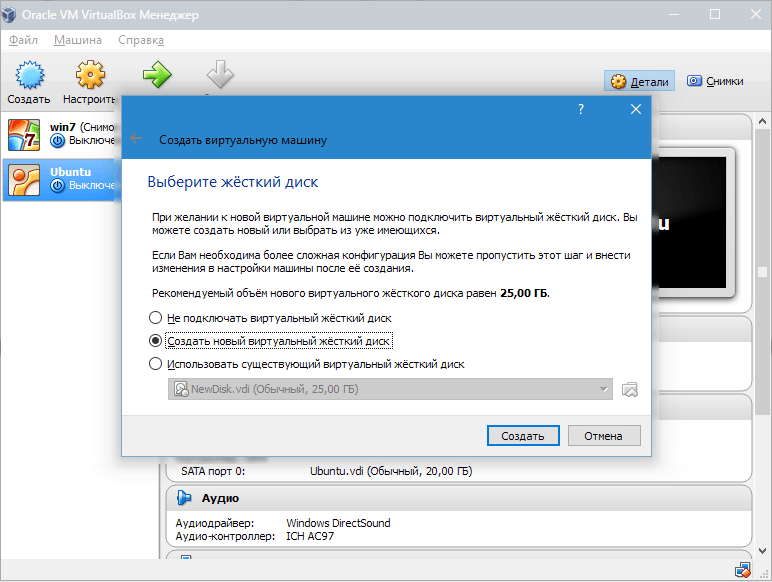
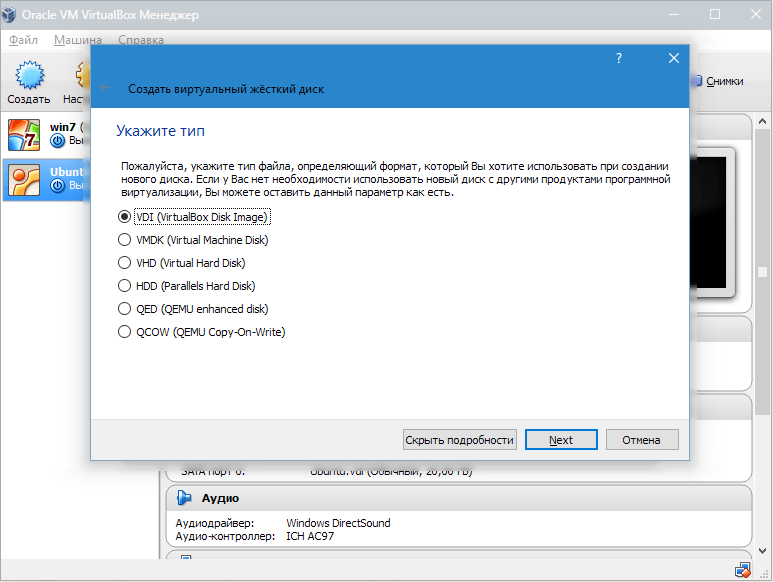
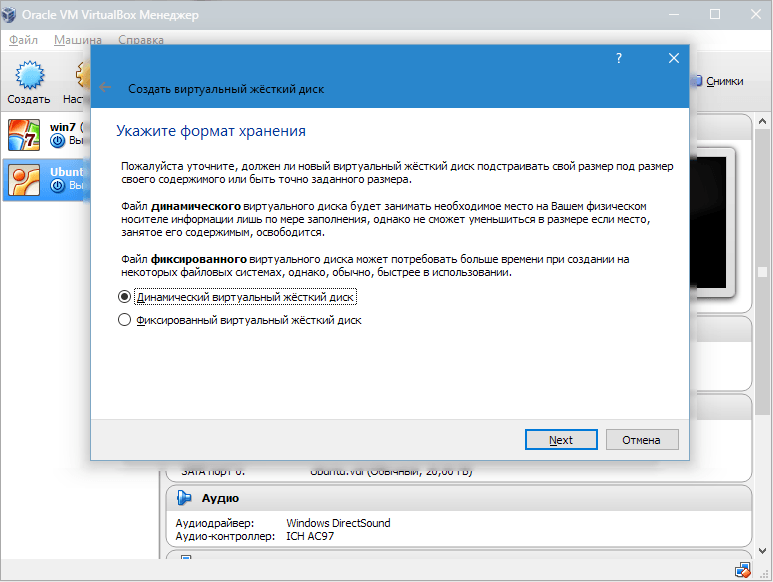
In a new window, you need to specify where the new disk image should be located and how large it is. If you are creating a boot disk containing Windows 7, then 25 GB is enough (this figure is set by default).
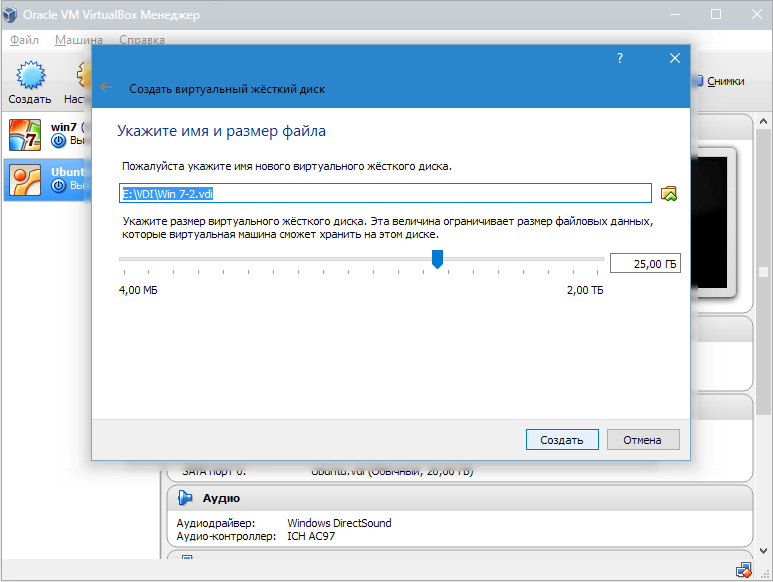
As for placement, it will place the drive outside of the system partition. Failure to do so may result in boot disk overload.
If everything suits, click "Create".
When the disk is created, the parameters of the created VM will be displayed in a new window.
Now you need to configure the hardware of the virtual machine.
![]()
In the "General" section, the 1st tab displays key information about the created machine.
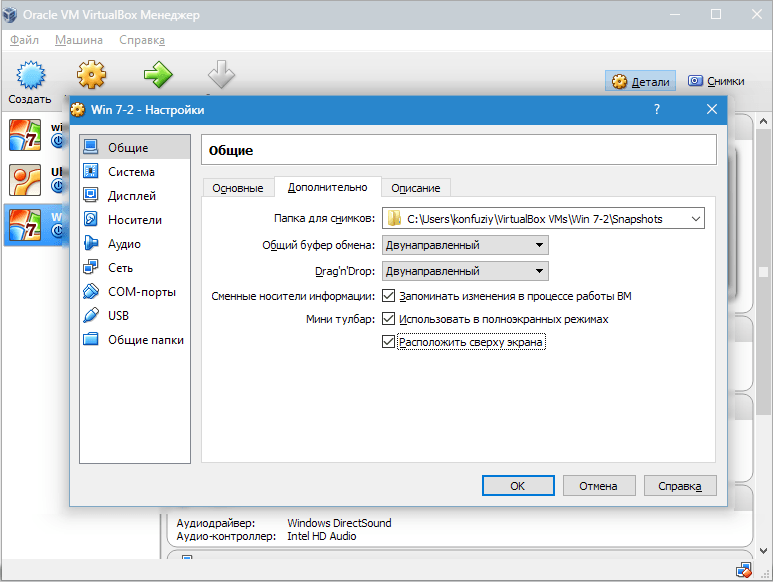
Let's open a tab "Additionally". Here we will see the option "Picture Folder". The specified folder is recommended to be placed outside the system partition, since the snapshots are large.
"Shared Clipboard" implies the operation of the clipboard when interacting with your host OS and VM. The buffer can work in 4 modes. In the first mode, the exchange is made only from the guest operating system to the main one, in the second - in the reverse order; the third option allows both directions, and the fourth disables communication. We choose the bidirectional option as the most convenient.
"Mini toolbar" is a small panel that allows you to manage the VM. We recommend activating this console in full-screen mode, since it completely repeats the main menu of the VM working window. The best place for it is at the top of the window, because that way there is no risk of accidentally pressing one of its buttons.
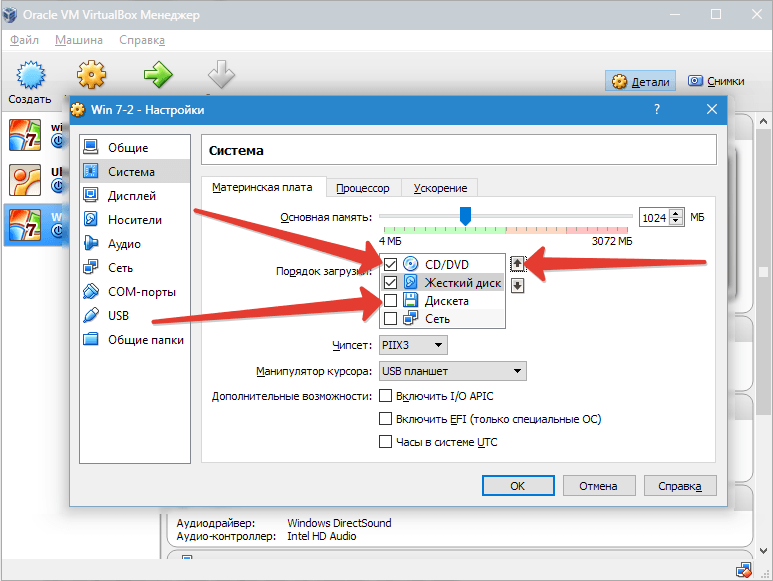
Let's go to the section "System". The first tab offers to make certain settings, which we will discuss below.
1. If necessary, adjust the amount of VM RAM. At the same time, only after its launch it will become completely clear whether the volume is chosen correctly.
When choosing, you should start from the amount of physical memory installed on the computer. If it is equal to 4 GB, then it is recommended to allocate 1 GB for the VM - it will function without "brakes".
2. Let's determine the order of loading. A floppy disk (floppy) player is not needed, turn it off. The first in the list should be assigned a CD / DVD drive in order to be able to install the OS from a disk. Note that this can be either a physical disk or a virtual image.
See the reference section for other settings. They are closely related to the hardware configuration of your computer. If you set settings that are not consistent with it, the VM will not start.
Bookmark "CPU" the user specifies how many cores are on the virtual motherboard. This option will be available if hardware virtualization is supported. AMD-V or VT-x.
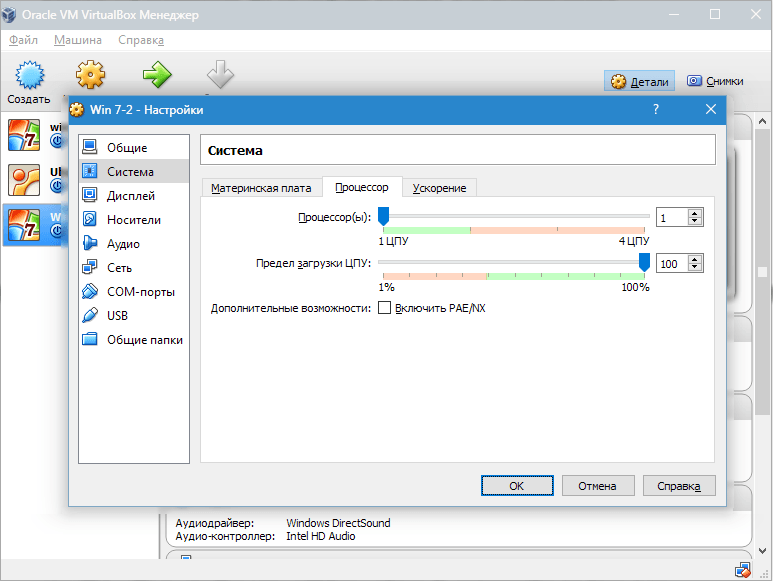
Regarding hardware virtualization options AMD-V or VT-x, then before activating them, you need to find out if these functions are supported by the processor and whether they are originally included in BIOS– it often happens that they are disabled.
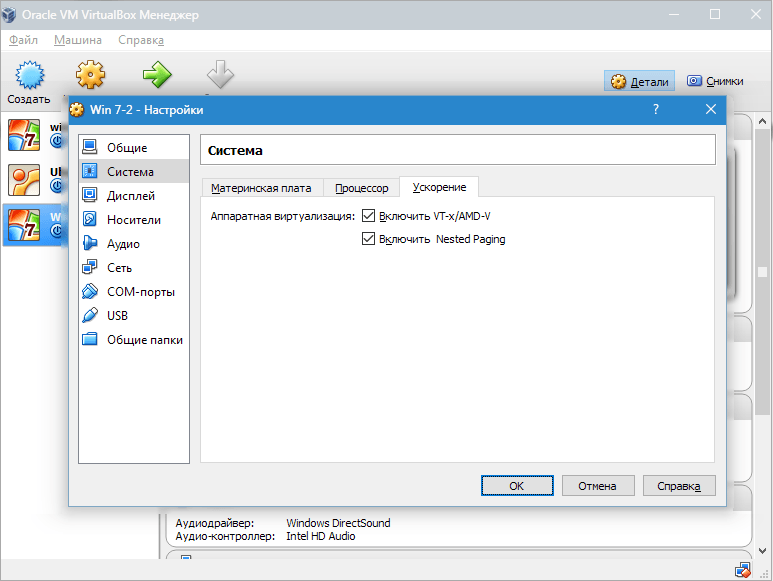
Now consider the section "Display". Bookmark "Video" indicates the amount of memory of the virtual video card. Activation of two-dimensional and three-dimensional acceleration is also available here. The first of them is desirable to include, and the second parameter is optional.
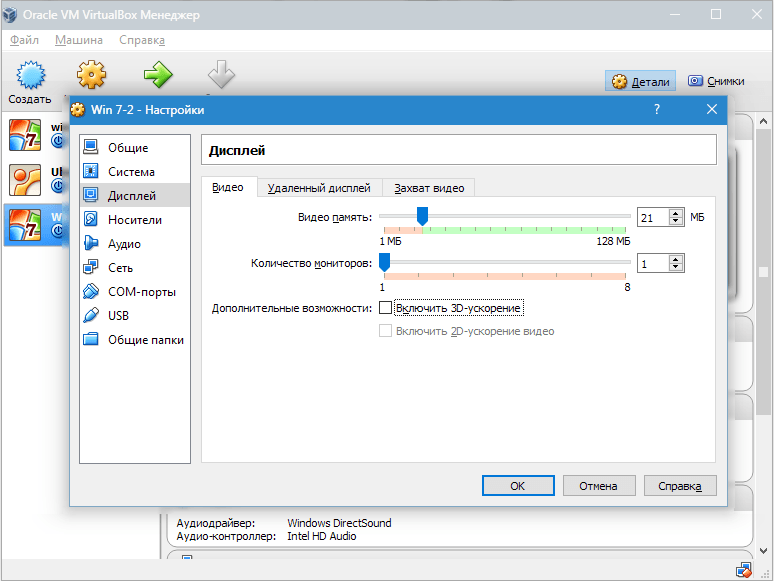
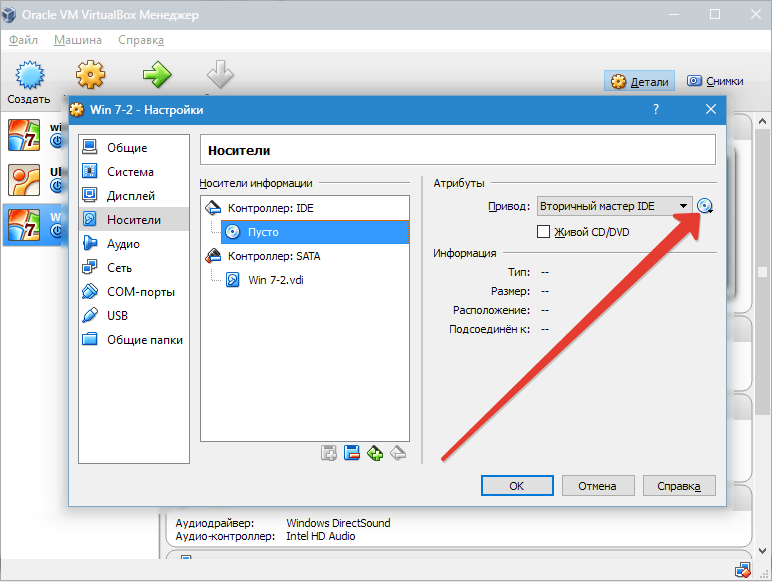
In chapter "Carriers" all disks of the new virtual machine are displayed. Also here you can see a virtual drive with the inscription "Empty". We will mount the Windows 7 installation disk image into it.
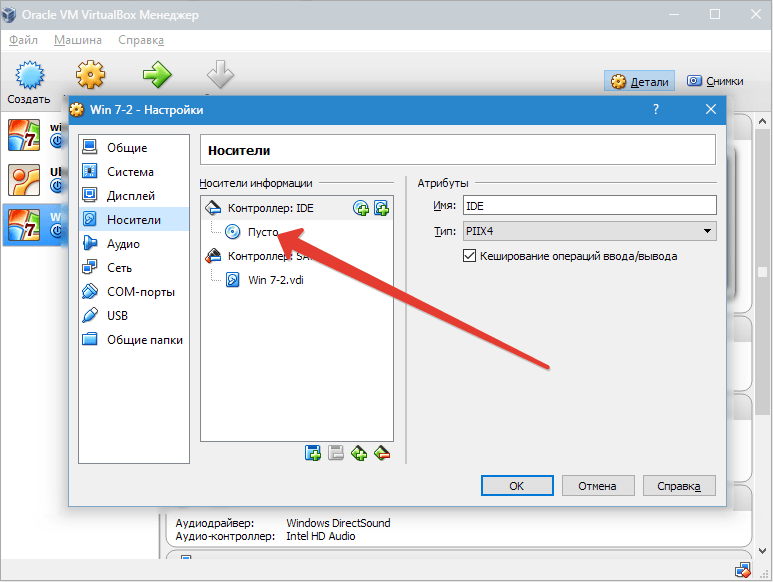
The virtual drive is configured as follows: click on the icon located on the right. A menu opens in which we click "Select optical disc image". The next step is to add the operating system boot disk image.
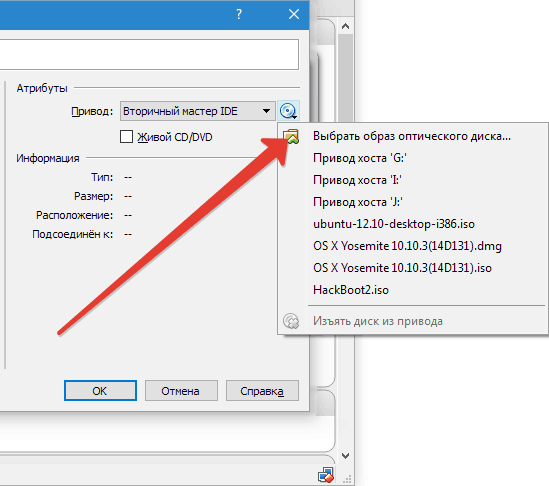
We will not cover network issues here. Note that the network adapter is initially active, which is a prerequisite for the VM to access the Internet.
On the section COM there is no point in dwelling in detail, since nothing is connected to such ports today.
In chapter USB check both available options.
Let's go to "Shared Folders" and select the directories to which the VM is planned to provide access.
The entire setup process is now complete. Now you can start installing the OS.
Select the created machine in the list and click "Run". The installation of Windows 7 on VirtualBox itself is very similar to a regular Windows installation.
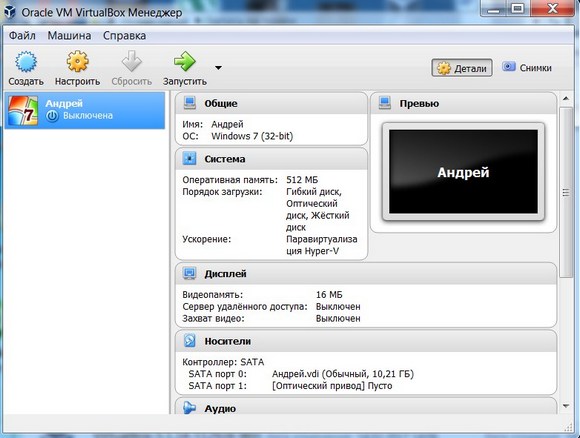
Windows 7 in English and the created virtual machine are ready to run.
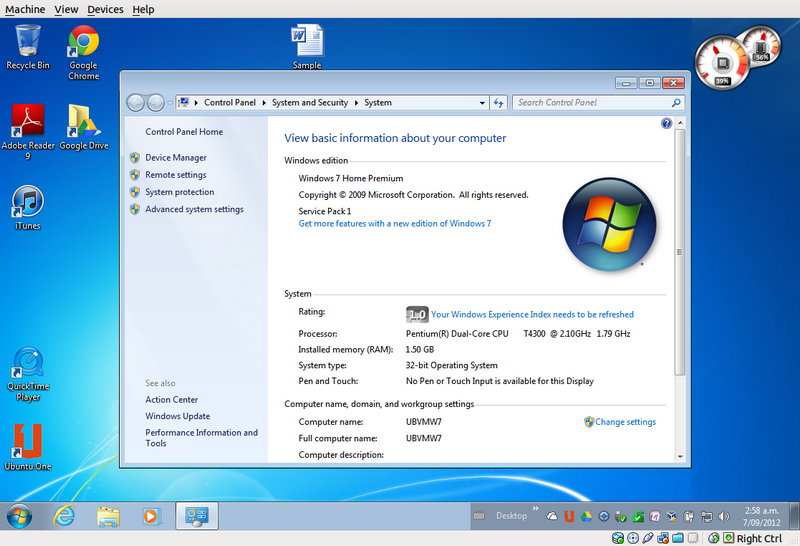
Set up a virtual system
All VM controls are intuitive. But if you have any questions, you should carefully read the tooltips in Russian. You can turn to help for help, where you can find answers to all questions.
Usually, both the mouse and the keyboard only work in the VM and are blocked in real Windows. But it is possible to switch between the two systems using the Right Control host key.
Now that the virtual machine is installed and running, you can configure Windows. The first step is to install software components (drivers) for all virtual devices. This process is quite simple. You need to go to the main menu and in the line " Devices" click on " Install Guest Additions».
After the installation is complete, the VM is rebooted. Now the picture has become clearer, the VM window can be dynamically changed, support for mouse integration will be connected, and Internet access will open.
There is also the possibility of extending the function of the displays. In this mode, windows that are opened in the VM will be displayed on the real desktop, and not in a separate program window. This makes it possible to facilitate access to all controls and installed programs of the VM.
Shutdown virtual Windows 7
Like a real laptop in a VM, Windows installed requires a certain order to be completed. You can end the job by pressing the button to stop the job. A menu will open with three options for closing the VM.
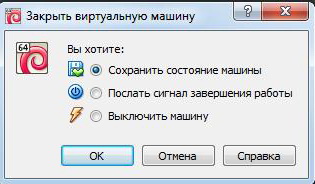
« Save machine state» - before shutting down, the machine will save all running applications at the time of shutdown. When the VM is turned on again, work in it can be continued from the moment it was turned off.
« Send a shutdown signal» - all applications can be closed and the machine will turn off automatically.
« Turn off the car” - just as if a real computer were de-energized.
Conclusion
From this short review, it can be seen that working with virtual machines, such as, makes it possible to connect several different operating systems at once on one device. Naturally, the more powerful the real device (RAM and CPU), the faster virtual computers will work. Disabling the antivirus on the native machine or if it is on the exclusion list will also help speed up the work.
