Sooner or later (better, of course, if early) any user asks himself the question of how long the installed on his computer will last HDD Isn't it time to look for a replacement? There is nothing surprising in this, since hard drives, due to their design features, are the least reliable among computer components. At the same time, it is on the HDD that most users store the lion's share of the most diverse information: documents, pictures, various software, etc., as a result of which an unexpected disk failure is always a tragedy. Of course, it is often possible to recover information on externally “dead” hard drives, but it is possible that this operation will cost you a pretty penny, and it will cost you a lot of nerves. Therefore, it is much more effective to try to prevent data loss.
How? Very simple ... First, do not forget about the regular backup data, and secondly, monitor the status of disks using specialized utilities. We will consider several programs of such a plan in terms of the tasks to be solved in this article.
Control of SMART parameters and temperature
All modern HDDs and even solid state drives (SSDs) support S.M.A.R.T. ( from English. Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology - technology of self-monitoring, analysis and reporting), which was developed by major manufacturers hard drives to improve the reliability of their products. This technology is based on continuous monitoring and assessment of the state hard drive built-in self-diagnostic equipment (special sensors), and its main purpose is the timely detection of a possible drive failure.
HDD status monitoring in real time
A number of information and diagnostic solutions for hardware diagnostics and testing, as well as special monitoring utilities, use S.M.A.R.T. to monitor the current status of various vital parameters that describe the reliability and performance of hard drives. They read the relevant parameters directly from the sensors and thermal sensors that all modern hard drives are equipped with, analyze the received data and display them in the form of a concise tabular report with a list of attributes. At the same time, some of the utilities (Hard Drive Inspector, HDDlife, Crystal Disk Info, etc.) are not limited to displaying a table of attributes (the values of which are incomprehensible to unprepared users) and additionally display brief information about the state of the disk in a more understandable form.
Diagnosing the condition of a hard drive using this kind of utilities is as easy as shelling pears - just get acquainted with brief basic information about installed HDDs: with basic data about disks in Hard Drive Inspector, a certain conditional percentage of hard disk health in HDDlife, the "Technical condition" indicator in Crystal Disk Info ( Fig. 1), etc. Any of these programs provides the minimum necessary information about each of the HDDs installed on the computer: data on the hard drive model, its volume, operating temperature, hours worked, as well as the level of reliability and performance. This information makes it possible to draw certain conclusions about the performance of the carrier.
Rice. 1. Brief information about the "health" of the working HDD
You should configure the launch of the monitoring utility at the same time as the operating system starts, adjust the time interval between checks of S.M.A.R.T. attributes, and enable display of the temperature and “health level” of hard drives in the system tray. After that, to control the status of disks, the user will only need to glance at the indicator in the system tray from time to time, where it will be displayed short information about the state of the drives available in the system: their level of "health" and temperature (Fig. 2). By the way, the operating temperature is no less important indicator than the conditional indicator of HDD health, because hard drives can suddenly fail due to banal overheating. Therefore, if the hard drive heats up above 50 ° C, then it would be wiser to provide it with additional cooling.

Rice. 2. HDD status display
in the system tray program HDDlife
It should be noted that some of these utilities provide integration with Windows Explorer, so that local disk icons display a green icon if they are healthy, and the icon turns red if problems occur. So you are unlikely to be able to forget about the health of your hard drives. With such constant monitoring, you will not be able to miss the moment when some problems begin to arise with the disk, because if the utility detects critical changes in the S.M.A.R.T. and / or temperature, it will carefully notify the user about this (by a message on the screen, a sound message, etc. - Fig. 3). Thanks to this, it will be possible to have time to copy the data from the medium that inspires fear in advance.

Rice. 3. An example of a message about the need to immediately replace the disk
Using S.M.A.R.T. monitoring solutions in practice to monitor the status of hard drives is completely easy, because all such utilities work in the background and require a minimum of hardware resources, so their operation will in no way interfere with the main workflow.
Control of S.M.A.R.T. attributes
Advanced users, of course, are unlikely to limit themselves to assessing the state of hard drives by viewing a brief verdict of one of the utilities presented above. It is understandable, because by decoding the attributes of S.M.A.R.T. it is possible to identify the cause of failures and, if necessary, prudently take some additional measures. True, to independently control S.M.A.R.T. attributes, you will need to at least briefly familiarize yourself with the S.M.A.R.T.
HDDs that support this technology include intelligent self-diagnosis routines so they can "report" their current status. This diagnostic information is provided as a collection of attributes, i.e. specific hard drive characteristics used to analyze its performance and reliability.
B about Most of the important attributes have the same meaning for drives from all manufacturers. The values of these attributes during normal disk operation may vary within certain intervals. For any parameter, the manufacturer has defined a certain minimum safe value that cannot be exceeded under normal operating conditions. Unambiguously determine critical and non-critical S.M.A.R.T parameters for diagnostics. problematic. Each of the attributes has its own informational value and indicates one or another aspect in the work of the carrier. However, first of all, you should pay attention to the following attributes:
- Raw Read Error Rate - frequency of errors in reading data from the disk due to the fault of the equipment;
- Spin Up Time - average spin up time of the disk spindle;
- Reallocated Sector Count - number of sector remapping operations;
- Seek Error Rate - frequency of occurrence of positioning errors;
- Spin Retry Count - the number of retries to spin up disks to operating speed if the first attempt fails;
- Current Pending Sector Count - the number of unstable sectors (that is, sectors waiting for the remapping procedure);
- Offline Scan Uncorrectable Count - total number of uncorrected errors during sector read/write operations.
Typically, S.M.A.R.T. are displayed in a tabular form with the attribute name (Attribute), its identifier (ID) and three values: current (Value), minimum threshold (Threshold) and the low value attribute for the entire time of the drive (Worst), as well as the absolute value of the attribute (Raw). Each attribute has a current value, which can be any number between 1 and 100, 200, or 253 (there is no general standard for upper bounds on attribute values). The Value and Worst values for a completely new hard drive are the same (Fig. 4).

Rice. 4. Attributes of S.M.A.R.T. on the new HDD
Shown in fig. 4 information allows us to conclude that for a theoretically sound hard drive, the current (Value) and worst (Worst) values should be as close to each other as possible, and the Raw value for most parameters (with the exception of the parameters: Power-On Time, HDA Temperature and some others ) should be close to zero. The current value may change over time, which in most cases reflects deterioration hard drive described by the attribute. This can be seen in fig. 5, which shows fragments of the S.M.A.R.T attribute table. for the same disk - the data are received with an interval of half a year. As you can see, in a more recent version of S.M.A.R.T. increased error rate when reading data from the disk (Raw Read Error Rate), the origin of which is due to the hardware of the disk, and the error rate when positioning the block of magnetic heads (Seek Error Rate), which may indicate overheating of the hard drive and its unstable position in the basket . If the current value of any attribute approaches or becomes less than the threshold, then the hard drive is considered unreliable, and it should be urgently replaced. For example, a drop in the value of the Spin-Up Time attribute (the average spin-up time of the disk spindle) below a critical value, as a rule, indicates complete wear of the mechanics, as a result of which the disk is no longer able to maintain the rotation speed specified by the manufacturer. Therefore, it is necessary to monitor the state of the HDD and periodically (for example, once every 2-3 months) carry out S.M.A.R.T. and save the received information in text file. In the future, these data can be compared with the current ones and certain conclusions can be drawn about the development of the situation.

Rice. 5. S.M.A.R.T. Attribute Tables Obtained at Semi-Annual Intervals
(more fresh version S.M.A.R.T. at the bottom)
When viewing S.M.A.R.T. attributes, you should first of all pay attention to critical important parameters, as well as on the parameters highlighted by indicators other than the base color (usually blue or green). Depending on the current state of the attribute in the S.M.A.R.T. in the table, it is usually marked in one color or another, which makes it easier to understand the situation. In particular, in the Hard Drive Inspector program, the color indicator can be green, yellow-green, yellow, orange or red - green and yellow-green colors indicate that everything is fine (the attribute value did not change or changed insignificantly), and yellow, orange and red colors signal danger (worst of all is red, which indicates that the value of the attribute has reached its critical value). If any of the critical parameters is marked with a red icon, then you need to urgently replace the hard drive.
Let's look at the table of S.M.A.R.T. attributes of the same disk in the Hard Drive Inspector program, a brief assessment of which by monitoring utilities was given earlier. From fig. 6 shows that the values of all attributes are normal and all parameters are marked in green. The HDDlife and Crystal Disk Info utilities will show a similar picture. True, more professional solutions for HDD analysis and diagnostics are not so loyal and often label S.M.A.R.T. attributes more meticulously. For example, such well-known utilities as HD Tune Pro and HDD Scan, in our case, were suspicious of the UltraDMA CRC Errors attribute, which displays the number of errors that occur when information is transmitted via the external interface (Fig. 7). The cause of such errors is usually associated with a twisted and poor-quality SATA cable, which may need to be replaced.

Rice. 6. Table of S.M.A.R.T. attributes obtained in the Hard Drive Inspector program

Rice. 7. Results of assessing the state of S.M.A.R.T. attributes
HD Tune Pro and HDD Scan utilities
For comparison, let's get acquainted with the S.M.A.R.T. attributes of a very ancient, but still working HDD with intermittent problems. He did not inspire confidence in the Crystal Disk Info program - in the "Technical Condition" indicator, the state of the disk was rated as alarming, and the Reallocated Sector Count attribute (Reassigned sectors) turned out to be highlighted in yellow (Fig. 8). This is a very important attribute from the point of view of the "health" of the disk, indicating the number of sectors remapped when the disk detects a read / write error, during this operation, data from the bad sector is transferred to the spare area. The yellow color of the indicator next to the parameter indicates that there are not enough remaining spare sectors with which to replace the bad ones, and soon there will be nothing to reassign the newly emerging bad sectors. Let's also check how more serious solutions evaluate the state of a disk, for example, the HDDScan utility widely used by professionals - but here we see exactly the same result (Fig. 9).

Rice. 8. Evaluate a problematic hard drive in CrystalDiskInfo

Rice. 9. Results of HDD S.M.A.R.T. diagnostics in HDDScan
This means that it is clearly not worth pulling with the replacement of such a hard drive, although it can also serve for some time, though the operating system is on given hard Of course, you can't install a disk. It should be noted that in the presence of a large number of reassigned sectors, the read / write speed drops (due to unnecessary movements that the magnetic head has to make), and the disk starts to noticeably slow down.
Surface scanning for bad sectors
Unfortunately, in practice, one control of SMART parameters and temperature is not enough. When there is the slightest evidence that something is wrong with the disk (in the case of periodic program freezes, for example, when saving results, reading error messages, etc.), you need to scan the disk surface for unreadable sectors. To carry out such a check of the media, you can use, for example, the HD Tune Pro and HDDScan utilities or diagnostic utilities from hard drive manufacturers, however, these utilities only work with their hard drive models, and therefore we will not consider them.
When using such solutions, there is a risk of data corruption on the scanned disk. On the one hand, with the information on the disk, if the drive really turns out to be faulty, anything can happen during the scan. On the other hand, it is impossible to exclude incorrect actions on the part of the user, who mistakenly starts scanning in write mode, during which sector-by-sector overwriting of data from the hard drive with a certain signature occurs, and based on the speed of this process, a conclusion is made about the state of the hard disk. Therefore, compliance with certain precautionary rules is absolutely necessary: before starting the utility, you need to create a backup copy of the information and, during the check, act strictly according to the instructions of the developer of the corresponding software. To get more accurate results before scanning, it is better to close all active applications and unload possible background processes. In addition, it should be borne in mind that if you need to test the system HDD, you need to boot from a flash drive and start the scanning process from it, or completely remove the hard drive and connect it to another computer from which to start testing the disk.
As an example, using HD Tune Pro, we will check the surface of the HDD for bad sectors, which above did not inspire confidence in the Crystal Disk Info utility. In this program, to start the scanning process, just select desired disk, activate tab error scan and click on the button start. After that, the utility will start sequentially scanning the disk, reading sector by sector and marking sectors on the disk map with multi-colored squares. The color of the squares, depending on the situation, can be green (normal sectors) or red (bad blocks), or it will have some shade intermediate between these colors. As we see from fig. 10, in our case, the utility did not find full-fledged bad blocks, but nevertheless, there is a solid number of sectors with one or another read delay (judging by their color). In addition to this, in the middle part of the disk there is a small block of sectors, the color of which is close to red - these sectors have not yet been recognized as bad by the utility, but they are already close to it and will go into the category of bad ones in the very near future.

Rice. 10. Scanning the surface for bad sectors in HD Tune Pro
Testing the media for bad sectors in the HDDScan program is more difficult, and even more dangerous, because in the case of an incorrectly selected mode, the information on the disk will be irretrievably lost. First of all, to start the scan, create new task by clicking the button New Task and selecting the command from the list Suface Tests. Then you need to make sure that the mode is selected read- this mode is set by default and when it is used, the hard disk surface is tested by reading (that is, without deleting data). After that press the button Add test(Fig. 11) and double click on the created task RD Read. Now in the window that opens, you can observe the process of scanning the disk on the graph (Graph) or on the map (Map) - fig. 12. Upon completion of the process, we will get approximately the same results that were demonstrated above by the HD Tune Pro utility, but with a clearer interpretation: there are no bad sectors (they are marked in blue), but there are three sectors with a response time of more than 500 ms (marked in red color), which represent a real danger. As for the six orange sectors (response time from 150 to 500 ms), this can be considered within the normal range, since such a response delay is often caused by temporary interference in the form of, for example, running background programs.

Rice. 11. Run a disk test in HDDScan

Rice. 12. Results of scanning a disk in Read mode using HDDScan
In addition, it should be noted that if there are a small number of bad blocks, you can try to improve the condition of the hard disk by removing bad sectors by scanning the disk surface in linear recording mode (Erase) using the HDDScan program. After such an operation, the disk can still be used for some time, but, of course, not as a system disk. However, one should not hope for a miracle, since the HDD has already begun to crumble, and there are no guarantees that in the near future the number of defects will not increase and the drive will not completely fail.
Programs for S.M.A.R.T.-monitoring and HDD testing
HD Tune Pro 5.00 and HD Tune 2.55
Developer: EFD Software
Distribution size: HD Tune Pro - 1.5 MB; HD Tune - 628 KB
Work under control: Windows XP/Server 2003/Vista/7
Distribution method: HD Tune Pro - shareware (15 day demo); HD Tune - freeware (http://www.hdtune.com/download.html)
Price: HD Tune Pro - $34.95; HD Tune - free (for non-commercial use only)
HD Tune is a handy utility for diagnosing and testing HDD/SSD (see table), as well as memory cards, USB drives and a number of other storage devices. The program displays detailed information about the drive (firmware version, serial number, disk space, buffer size, and transfer mode) and allows you to set the device status using S.M.A.R.T. and temperature monitoring. In addition, it can be used to test the disk surface for errors and evaluate the performance of the device by conducting a series of tests (sequential and random read / write speed tests, file performance test, cache test and a number of Extra tests). Also, the utility can be used to set up AAM and securely delete data. The program is presented in two editions: commercial HD Tune Pro and free lightweight HD Tune. In the HD Tune edition, only viewing detailed information about the disk and the S.M.A.R.T. attribute table is available, as well as scanning the disk for errors and testing for speed in read mode (Low level benchmark - read).
The Health tab is responsible for monitoring S.M.A.R.T. attributes in the program - data is read from the sensors after a set period of time, the results are displayed in the table. For any attribute, you can view the history of its changes in numerical form and on a graph. Monitoring data is automatically logged, but no user notifications are provided for critical parameter changes.
As for scanning the disk surface for bad sectors, the tab is responsible for this operation. error Scan. Scanning can be fast (Quick scan) and deep - with quick check not the entire disk is scanned, but only some part of it (the scan area is determined through the Start and End fields). Bad sectors are displayed on the disk map as red blocks.
HDDScan 3.3
Developer: Artem Rubtsov
Distribution size: 3.64 MB
Work under control: Windows 2000(SP4)/XP(SP2/SP3)/Server 2003/Vista/7
Distribution method: freeware (http://hddscan.com/download/HDDScan-3.3.zip)
Price: is free
HDDScan is a utility for low-level diagnostics of hard drives, solid state drives and USB flash drives. The main purpose of this program is to test disks for bad blocks and bad sectors. Also, the utility can be used to view the contents of S.M.A.R.T., monitor temperature and change some hard drive settings: noise management (AAM), power management (APM), forced start / stop of the drive spindle, etc. The program works without installation and can be launched from portable media, like flash drives.
Display of S.M.A.R.T. attributes and temperature monitoring in HDDScan is done on demand. S.M.A.R.T. report contains information about the performance and "health" of the drive in the form of a standard attribute table, the temperature of the drive is displayed in the system tray and in a special information window. Reports can be printed or saved as an MHT file. S.M.A.R.T. tests are possible.
Checking the disk surface is performed in one of four modes: Verify (linear verification mode), Read (linear reading), Erase (linear writing) and Butterfly Read (Butterfly reading mode). To check the disk for the presence of bad blocks, a test in Read mode is usually used, with the help of which the surface is tested without deleting data (a conclusion about the state of the drive is made based on the speed of sector-by-sector data reading). When testing in the linear recording mode (Erase), the information on the disk is overwritten, but this test can somewhat heal the disk, ridding it of bad sectors. In any of the modes, you can test the entire disk or a certain fragment of it (the scanning area is determined by specifying the initial and final logical sectors - Start LBA and End LBA, respectively). The test results are presented in the form of a report (Report tab) and displayed on a graph (Graph) and a disk map (Map) indicating, among other things, the number of bad sectors (Bads) and sectors whose response time during testing took more than 500 ms (marked in red ).
Hard Drive Inspector 4.13
Developer: AltrixSoft
Distribution size: 2.64 MB
Work under control: Windows 2000/XP/2003 Server/Vista/7
Distribution method: shareware (14-day demo - http://www.altrixsoft.com/ru/download/)
Price: Hard Drive Inspector Professional - 600 rubles; Hard Drive Inspector for Notebooks - 800 rubles.
Hard Drive Inspector is a handy solution for S.M.A.R.T. monitoring of external and internal HDDs. At the moment, the program is offered on the market in two editions: the basic Hard Drive Inspector Professional and the portable Hard Drive Inspector for Notebooks; the latter includes all the functionality of the Professional version, and at the same time takes into account the specifics of monitoring laptop hard drives. Theoretically, there is another version of the SSD, but it is distributed only in OEM deliveries.
The program provides automatic verification of S.M.A.R.T. attributes at specified intervals and, upon completion, issues its verdict regarding the state of the drive, displaying the values of certain conditional indicators: "reliability", "performance" and "no errors" along with a numerical temperature value and a temperature diagram. It also provides technical data about the drive model, capacity, total free space and operating time in hours (days). In advanced mode, you can view information about disk parameters (buffer size, firmware name, etc.) and the S.M.A.R.T attribute table. There are various options for informing the user in case of critical changes on the disk. Additionally, the utility can be used to reduce the noise level produced by hard drives and reduce the power consumption of the HDD.
HD Life 4.0
Developer: BinarySense Ltd.
Distribution size: 8.45 MB
Work under control: Windows 2000/XP/2003/Vista/7/8
Distribution method: shareware (15-day demo - http://hddlife.ru/rus/downloads.html)
Price: HDDlife - free; HDDLife Pro - 300 rubles; HDDlife for Notebooks - 500 rubles.
HDDLife- simple utility, designed to monitor the status of hard drives and SSDs (from version 4.0). The program is presented in three editions: free HDDLife and two commercial editions - basic HDDLife Pro and portable HDDlife for Notebooks.
The utility monitors S.M.A.R.T. attributes and temperature at specified intervals and, based on the results of the analysis, issues a compact report on the state of the disk, indicating technical data on the disk model and its capacity, hours worked, temperature, and also displays the conditional percentage of its health and performance, which allows to navigate the situation even for beginners. More experienced users can additionally look at the table of S.M.A.R.T. attributes. In case of problems with hard drive it is possible to configure notifications; you can configure the program so that when the disk is in a normal state, the results of the check are not displayed. Level control possible HDD noise and energy consumption.
CrystalDiskInfo 5.4.2
Developer: Hiyohiyo
Distribution size: 1.79 MB
Work under control: Windows XP/2003/Vista/2008/7/8/2012
Distribution method: freeware (http://crystalmark.info/download/index-e.html)
Price: is free
CrystalDiskInfo is a simple S.M.A.R.T. external HDD) and SSD. Despite the freeware, the program has all the necessary functionality to organize disk health monitoring.
Disks are monitored automatically after a specified number of minutes or on demand. At the end of the test, the system tray displays the temperature of monitored devices; Detailed information about the HDD with S.M.A.R.T. values, temperature, and the program's verdict on the state of the devices is available in the main window of the utility. There is functionality to set threshold values for some parameters and automatically notify the user if they are exceeded. Noise level management (AAM) and power management (APM) are possible.
Unfortunately, a large part of modern HDDs work normally for a little over a year, then all sorts of problems begin, which over time can lead to data loss. Such a prospect can be completely avoided if you carefully monitor the condition of the hard drive, for example, using the utilities discussed in the article. However, you should not forget about regular backup of valuable data either, since monitoring utilities, as a rule, successfully predict the failure of a disk due to the fault of “mechanics” (according to Seagate statistics, about 60% of HDDs fail due to mechanical components), but they are not able to predict the death of the drive due to problems with electronic components disk.
Good day!
How much could be corrected if we knew in advance what awaits us ...
And if in life it is almost impossible to predict some events, then in the case of a hard drive - some of the problems are still possible to predict and foresee!
For this there are special utilities, who can find out and analyze the SMART * readings of the disk (show them to you if necessary), and based on these data, evaluate the health of your disk, simultaneously calculating how many years it can still last.
The information is extremely useful, besides, such utilities can monitor your disk online, and as soon as the first signs of unstable operation appear, they will immediately notify you. Accordingly, you will have time to make a backup and take action (although you should always make a backup, even when everything is fine 😊).
And so, in the article I will consider several ways (and several utilities) to analyze the state of the HDD and SSD.
* Note:
S.M.A.R.T. (Self-Monitoring, Analysis and Reporting Technology) - a special technology for assessing the condition of a hard disk by an integrated hardware self-diagnosis / self-monitoring system. The main task is to determine the probability of a device failure, preventing data loss.
Perhaps this is one of the most popular questions asked by all users who first encountered problems with a hard drive (or thought about the security of storing their data). Everyone is interested in the time that the disk will work until it completely "stops". Let's try to predict...
Therefore, in the first part of the article, I decided to show a couple of utilities that can get all the readings from the disk and analyze them on their own, and give you only the finished result (in the second part of the article, I will give utilities for viewing SMART readings for self-analysis).
Method #1: Using Hard Disk Sentinel
One of the best utilities for monitoring the status of computer disks (both hard drives (HDD) and "newfangled" SSDs). What is most captivating in the program is that it will independently analyze all the data received on the state of the disk and show you the finished result (very convenient for novice users).
In order not to be unfounded, I will immediately show the main window of the program, which appears after the first launch (the analysis of the disk will be done immediately automatically). The health and performance of the disk is estimated as 100% (ideally, it should be), the time that the disk will still work in normal mode is estimated by the program at about 1000 days (~3 years).

What's up with the hard disk according to the Hard Disk Sentinel
In addition, the program allows you to monitor the temperature: both the current and the average and maximum during the day, week, month. If the temperature goes beyond the "normal" - the program will warn you about it (which is also very convenient).
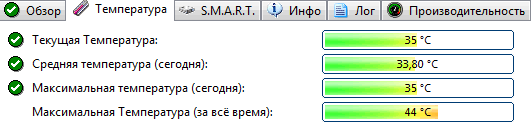
Hard Disk Sentinel also allows you to view SMART readings (however, in order to evaluate them, you need to have a good understanding of disks), get full information about the hard drive (model, serial number, manufacturer, etc.), see what the hard drive is loaded with (i.e. get performance information).
In general, in my humble opinion, Hard Disk Sentinel is one of the best utilities for monitoring the status of disks in the system. It is worth adding that there are several versions of the programs: professional and standard (for a professional version with advanced functionality, there is a portable version of the program that does not need to be installed (for example, it can even be run from a USB flash drive)).
Hard Disk Sentinel works in all popular Windows (7, 8, 10 - 32|64 bits), supports the Russian language in full.
Method number 2: using HDDlife
This program is similar to the first one, it also clearly shows the current state of the disk: its health and performance (in percentage terms), its temperature, the amount of time worked (in months). At the top of the window, based on all this data, HDDlife shows a final summary of your disk, for example, in my case "ALL RIGHT" (which means that everything is fine with the disk).
By the way, the program can work online, monitoring the status of your disk, and in case something goes wrong (when the first signs of problems appear), it will immediately notify you about it.
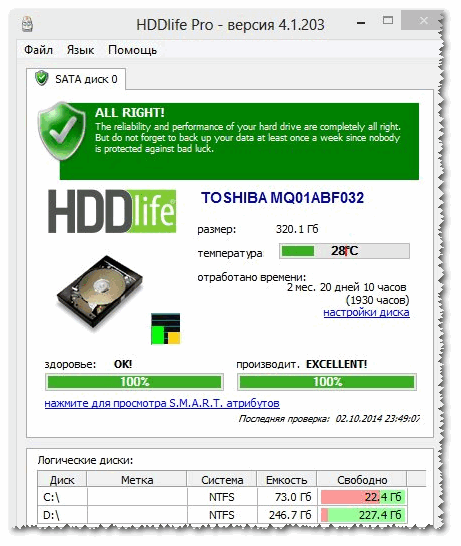
As an example, the screenshot below shows the SSD received a warning: its condition is still within acceptable limits, but reliability and performance are below average. In this case, you should not trust the disk with any important data, and if possible, you need to prepare to replace it.

By the way, in the main window of the program, next to the amount of disk time worked, there is a link "Disk Adjustment" (allows you to change some necessary parameters). By opening it, you can control the balance between noise / performance (very useful with drives that are very noisy), and adjust the power consumption settings (relevant for laptops that run out of battery quickly).

Addendum: HDDlife works on both PCs and laptops. Supports HDD and SSD drives. There are portable versions of the program that do not need to be installed. You can set it up so that the program starts with your Windows. HDDlife runs on Windows: XP, 7, 8, 10 (32|64 bits).
How to view SMART readings
If the previous utilities independently assessed the state of the disk, based on SMART data, then the utilities below will provide you with more freedom and data for self-analysis. It will be possible to find a fairly large set of parameters in the reports, on the basis of which it will be possible to roughly assess the state of the disk and make a forecast for its further operation.
Method number 1: using CrystalDiskInfo
CrystalDiskInfo
Excellent free utility to view the status and SMART readings of the hard drive (including SSD drives are supported). What the utility captivates with is that it provides you with complete information about the temperature, the technical condition of the disk, its characteristics, etc. experienced users, who themselves know "what-is-what", and for beginners who need a hint).
For example, if something is wrong with the temperature, then you will see a red indicator on it, i.e. CrystalDiskInfo will tell you about it.

The main window of the program can be conditionally divided into 4 zones (see the screenshot above):
- "1" - here are all your physical disks installed in the computer (laptop). Next to each, its temperature, technical condition, and the number of sections on it are shown (for example, "C: D: E: F:");
- "2" - it shows the current temperature of the disk and its technical condition (the program makes an analysis based on all the data received from the disk);
- "3" - disk data: serial number, manufacturer, interface, rotation speed, etc.;
- "4" - SMART readings. By the way, what bribes the program - you do not need to know what this or that parameter means - if something is wrong with any item, the program will mark it in yellow or red and notify you about it.
As an example of the above, I will give a screenshot showing two disks: on the left - with which everything is fine, on the right - which has problems with reassigned sectors (technical condition - alarm!).

As a reference (about remapped sectors):
when a hard disk detects, for example, a write error, it transfers data to a specially designated spare area (and this sector will be considered “remapped”). Therefore, bad blocks cannot be seen on modern hard drives - they are hidden in remapped sectors. This process is called remapping, and the reassigned sector - remap.
The greater the value of the reassigned sectors, the worse the state of the disk surface. Field "raw value" contains the total number of remapped sectors.
By the way, for many disk manufacturers, even one reassigned sector is already a warranty case!
To utility CrystalDiskInfo monitored the status of your hard drive online - in the "Service" menu, check two boxes: "Start Agent" and "Autostart"(see screenshot below).

Then you will see the program icon with the temperature next to the tray clock. In general, now you can be more calm about the state of the disk ☺...

Method number 2: using Victoria
Victoria- one of the most famous programs for working with hard drives. The main purpose of the program is to evaluate the technical condition of the drive and replace bad sectors with backup working ones.
The utility is free and allows you to work both under Windows and under DOS (which in many cases shows much more accurate information about the state of the disk).
Of the minuses: it is quite difficult to work with Victoria, at least I strongly do not recommend pressing buttons in it at random (you can easily destroy all data on the disk).
I have one fairly simple article on my blog (for beginners), which explains in detail how to check a disk using Victoria (including, find out the SMART readings - an example in the screenshot below (in which Victoria pointed to possible problem with temperature).
👉 To help!
Quick disk diagnostics in Victoria:

A hard drive is a complex electronic-mechanical device that has its own self-diagnostic technology that can predict the imminent failure of your hard drive. Which is usually a very sad event...
Technology S.M.A.R.T.(English) S elf M monitoring A scribing and R eporting T echnology ) - a technology for assessing the state of a hard disk with built-in self-diagnostic equipment, as well as a mechanism for predicting the time of its failure.
We will not consider this technology in detail, because. this is too broad a question and each of the drive manufacturers has its own vision and the number of monitored parameters. Consider the most important from a practical point of view.
To do this, we need a program to view the monitored parameters.
In it, on the "Data storage-> SMART" tab, select the hard disk and the monitored parameters are displayed in the window:
01 Raw Read Error Rate- the number of reading errors. Modern disks have a very high data storage density, so they constantly read data with errors, and the information is restored due to the ECC error correction code. It is these errors that this parameter considers. These non-critical errors are shown in Seagate hard drives, while other manufacturers prefer to remain modestly silent about this. For Seagate drives, the state can be considered very good when the Raw Read Error Rate and Hardware ECC Recovered parameters are equal. This means that how many errors there were, so many were corrected using the correction code. If these values are not equal, then you should not be afraid. This is not a critical parameter and the disk can live for years without any problems.
03 Spinup Time- time to spin up the disk to a working state. You should only worry if the value is less than half of the initial value. But there are still a few nuances, such as how many platters are in the hard drive. The maximum at present is 5 platters (Hitachi), of course, it will take more time to spin up such a package of disks than for the 1st platter. Nobody canceled the force of inertia.
04 Start/Stop Count- total number of starts/stops of the spindle. For Seagate, the number of times the spindle stops when going into power save mode.
05 Reallocated Sector Count- number of reassigned sectors. That is, when a disk detects a read/write error, it marks the sector as "remapped", and transfers the data to a specially designated spare area. In general, this is a terrible parameter, if its value is more than 10, then this at least means that it is time to check the entire surface of the disk in order to understand whether this process will continue. Judging by practice, laptop disks suffer from reassigned sectors somewhere after a year of use. Because they work in very harsh conditions. I'm not talking about strikes - most are more or less protected from this. The reason is temperature. The laptop case is usually poorly ventilated and the drive overheats, then we turn off the laptop and go where? That's right, on the street! And it's -10 Celsius. That's just the rate of heating-cooling and destroys the delicate magnetic layer on the disc plates. According to the specifications of all disk manufacturers, the so-called "temporal temperature gradient", that is, the rate of temperature change should be no more than 20 degrees / hour - in working condition and no more than 30 degrees / hour in the off state. This rule is always violated, but for laptops it is especially often and cruelly.
09 Power-on Time Count (Power-on Hours)- the amount of time spent in the on state. Usually for modern drives it is measured in hours (for Fujitsu in seconds). For old Maxtor drives, not for those now produced by Seagate under this brand, but for original Maxtor drives, the time changes in minutes. This is very useful parameter if you buy an old disk, then you want to know how much it has worked in its life. And besides, this time usually coincides with the time of the computer and you can determine how many people spend at the computer on average. As practice and my survey on one of the major forums dedicated to computer hardware show, disks with an operating time of more than 20,000 hours (approximately 2.5 years of continuous operation) already have some kind of defects, for example, the same "reassigned" sectors and are not so far from senile death. From the same manufacturer's specifications, you can find out that desktop drives are not designed to work around the clock, but are designed to work in 8/5 mode, that is, 8 hours 5 days a week. This works out to about 2400 hours per year. And it turns out that the warranty is calculated for 3 years - 7200 hours, for 5 years - 12000 hours. Not so much, considering that there are 8760 hours in a year.
0A Spinup Retry Count- The number of retries to spin up disks to operating speed if the first attempt was unsuccessful. If the attribute value increases, then mechanical/bearing damage is likely. Very rare, modern discs are made with hydrodynamic bearings and in the event of a malfunction of such a bearing, it jams immediately and tightly or works happily ever after. Not so long ago, Toshiba drives suffered greatly from this, and to a lesser extent western digital. Jamming occurs from overheating.
0C Power Cycle Count- number of disk on/off cycles.
C2 Temperature- disk temperature. Unfortunately, the temperature sensors are on the disks. different manufacturers in different places, so there are both overestimations and underestimations of the real temperature. But on average, as shown by a recent Google study, the optimal operating temperature is in the range of 35 to 45 degrees. Above 50 degrees, operation is highly discouraged, but such temperatures and even higher can often be seen in laptops.
The number of sectors that are candidates for replacement. They have not yet been identified as bad, but reading from them is different from reading a stable sector, these are the so-called suspicious or unstable sectors. In the case of a successful subsequent reading of the sector, it is excluded from the list of candidates. In the event of repeated erroneous reads, the drive tries to recover it and performs a remapping operation. A non-zero value usually occurs if there are already remapped sectors on the disk. If this is the case, then with a high probability we can say that the disk is actively "stripping", that is, the magnetic layer of the hard disk platters is being destroyed.
The number of uncorrected errors, that is, severe damage to the disk surface. Such errors appear when the space in the reserve zone of the disk for sector remapping runs out. They can also appear when the power is suddenly turned off at the moment when the disk is writing data - these are the so-called "software bad blocks". If their number is one or two, and the rest of the parameters relating to the surface of the disk are normal, then you should not worry. If it is large, then the data must be saved and the "body to be taken out" should be prepared. :)
C7 Ultra ATA CRC Error Rate- number of transmission errors in the external interface. Usually the cable is to blame or poor contact of the cable with the connectors, especially manifested on SATA drives. Occurs quite often.
C8 Write Error Rate- Errors when writing to disk. Occurs rarely. Usually on very old discs. If there are errors, then this means the physical wear of the hard disk drive. Or with serious damage to the surface of the disk. (when the number of reassigned sectors and uncorrected errors exceeds all reasonable values).
So we briefly reviewed the main parameters of the hard drive self-diagnosis system. If you want to know more about this, you can refer to Wikipedia materials:
Unfortunately, SMART cannot always predict disk death. As the study of the same Google showed, about 50% of disks die abruptly and for no apparent reason. But in one this technology is definitely useful. Using it, you can quickly find out the state of the disk surface, that is, the parameters:
05 Reallocated Sector Count
C5 Current Pending Sector Count
C6 Offline Uncorrectable Sector Count
And it is very useful to know the time that a disk has worked in its life in order to roughly guess what you can expect from it.
And now a little about the future. A sufficient number of offers of really "hard drives" have already appeared on sale. They are made on flash-type solid-state memory chips and are much more reliable both in terms of mechanical stress and temperature. However, manufacturers have not yet agreed on a standard self-diagnostic system for this type of drive. But it will be much easier than for the good old electromechanical drives. And most importantly, it will predict the possibility of failure with a much higher probability! Flash memory is more predictable in this sense. Well, let's wait for this bright future!
Letter. Hello admin! Please answer me this question. I downloaded the HDDScan program to test the status of my almost new hard drive, this program has a tool that shows the S.M.A.R.T of my hard drive, the most important parameter in it Reallocated Sector Count (indicating the number of remapped bad sectors) shows the current value Value 100. The Threshold value, that is, the value below which you can not fall 36. Tell the admin, what is the state of this disk and is it worth using it, does it threaten me with data loss?
Here is another disk, but most likely it needs to be changed, is it?

HDDScan
Friends, the article you are reading now is a continuation of another one, and if I were you, I would first of all read it - in it we examined the numerous reasons for the formation of various bad blocks (bad sectors) on the hard disk and why some of them are fixable, while others do not, we also learned how information is applied to the ferromagnetic plates of a hard drive, what a sector is and much more.
In this article, we will work in the program HDDScan, using it, we will find out everything about the state of our hard drive, check it with various tests, find out the S.M.A.R.T indicators of this hard drive, find 63 logical bad sectors and fix them.
What is S.M.A.R.T.?
For a long time, the well-known company IBM in 1992 developed a technology that controls all the critical parameters of a hard drive and at the very beginning it was called Predictive Failure Analysis (PFA). Then in 1992, Compaq, Seagate, Quantum, Conner invented and proposed a more advanced IntelliSafe technology. And only in 1995, the largest hard drive manufacturers developed an improved technology that is still used today and is called S.M.A.R.T (from the English self-monitoring, analysis and reporting technology - self-monitoring, analysis and reporting technology).
Hard drives that support S.M.A.R.T technology have a built-in processor that keeps track of the hours worked by the hard drive, and also determines the number of bad sectors (bad blocks), temperature and much more, read in detail below.
To find out everything that S.M.A.R.T can tell us, you just need to run a program that can read all these indicators. There are quite a lot of similar programs and I want to say at one time I tried them all. HDDScan used too, convenient, simple, reliable and free, works without installation, so you can carry it with you on a flash drive. Go to the manufacturer's website
Many PC users hardly think about checking the status of their HDD. Checking the hard drive, first of all, is needed for early detection of errors.
If you manage to identify problems with the hard drive in advance, then you can save all the important information stored on it until it finally fails.
In this article, we will describe, using specific examples, the procedure for checking the status of the HDD, and also tell you what to do in a situation if your hard drive is faulty.
How to check the status of a hard drive
You can check the status of your hard drive using various utilities that read the status of your hard drive from its self-diagnosis system. SMART. SMART technology is now installed on every manufactured hard drive. SMART technology was developed back in 1992 and is still being improved to this day. The main task of SMART is logging of the hard drive aging process. That is, information such as the number of HDD activations, the number of spindle rotations and many others is being collected. More SMART looking for errors"screws", both software and mechanical, and as far as possible corrects them. During the monitoring process, SMART performs various tests such as short and long to identify those same faults. In this article, we will consider such programs that can read information from SMART:
- Ashampoo HDD Control 3;
- Defraggler;
- HD Life;
- Victoria.
Each program from the list, in addition to reading SMART readings, offers a number of functions, tests, which in one way or another extend the life of the hard drive. But the most interesting is the program Victoria. The Victoria program, in addition to determining the state of the HDD, also knows how to produce REMAP bad sectors. That is, she can hide bad sectors by replacing them with spare ones if they exist. In essence, the REMAP procedure can restore hard drive. It is also worth noting the possibility of fixing the hard drive thanks to the console application " chkdsk". The console program "chkdsk" can fix file system errors, which will allow you not to reinstall Windows.
Ashampoo HDD Control 3
We will first look at the program Ashampoo HDD Control 3. Let's run this utility on the computer under Windows control 10.
The Ashampoo HDD Control 3 window shows the message " ✓ OK", as well as the inscription " This hard drive has no problems". This information means that the hard drive in question is in perfect order. If you see the message " Error", as well as the inscription " This hard drive has a problem”, then this means that it has bad sectors or overheats. To view full information about the health of the "screw" taken from smart, you need to click on the footnote "" located in the central block.
In addition to viewing information from smart, Ashampoo HDD Control 3 can run self-test test S.M.A.R.T. and surface check test. You can test these tests in the "" block.

By performing these tests, you can also identify problems with the HDD. In addition to taking readings from smart and tests, Ashampoo HDD Control 3 can:
- Perform defragmentation;
- Clean up the system of debris;
- Find and remove duplicate files;
- Securely overwrite files from the HDD, without the possibility of recovery.
The presence of such Ashampoo HDD Control 3 functionality in monitoring the health of the screw and additional features puts utility first.
Defraggler
Utility Defraggler primarily intended for defragmentation, but besides that, she can read SMART readings. The utility is free and any user can download it from www.piriform.com. After starting the utility, you need to go to the tab " State».

The window shows that the utility displays a message about the state of the screw, as " GOOD' means he's fine. If you see the message " Error” in the status, this will mean that there are bad sectors on the hard drive and it is time to change it. The utility is quite simple and is suitable, first of all, for novice PC users who want to monitor the health of the HDD and defragment it. I would also like to note that the utility supports all current operating systems, from Windows XP to Windows 10.
How to check your hard drive with HDDlife
Utility HDDlife has a nice interface and immediately gives us the information we need, which is responsible for the serviceability and breakage of the screw.

From the image above, you can see that in the block health is " OK!", which means that everything is in order with the HDD. To see the details of smart, you just need to click on the link " click to view S.M.A.R.T. attributes».

If you see a message in the health block " DANGER!”, then this means that your HDD will soon become unusable.

In this case, you need to replace the old hard drive with a new one. The HDDlife utility, first of all, is suitable for novice PC users, as its simplicity will make it easy to monitor the health of the “screw”. In addition to the standard utility, the developer also releases HDDlife for Notebooks which is designed for laptops. The laptop version has the same functionality as the standard version, but can also HDD noise control. It is also worth noting that the program supports all current operating systems, from Windows XP to Windows 10.
Victoria
Program Victoria is being developed under DOS and by Windows. For our example, we will use the Windows version of Victoria, which can be downloaded from http://hdd-911.com. Victoria is currently available in version 4.47. By running the Victoria utility, we will get into such a window.

Victoria does not have a beautiful interface, as in previous utilities, and is written in such old languages as Delphi and assembler.
In the first tab of Victoria " Standard» is all information about installed hard drives into the computer.
Second tab " SMART» needed for smart reading. To display smart results, you must click the Get SMART button and the results will be displayed.

In the hard drive under consideration, Victoria found 1212 bad sectors. Such a number of BAD sectors is critical, so in this case it is necessary to carry out full backup all data from the HDD. To repair the hard drive with the REMAP test in Victoria, go to the tab " Tests» and select the mode « Remap". After these steps, you can start the reassignment procedure bad sectors to the backup button Start .

The REMAP test at Victoria can take a very long time. The test time depends on the number of bad sectors. This test of the Victoria utility does not always help, since there might not be any spare sectors left in the "screw".
Please note that using Victoria tests, you can damage the health of the HDD and the information on it.
How to check the disk for health using "chkdsk"
It may happen that by checking the S.M.A.R.T. using the utilities described above, you did not find any problems, but the system still behaves unstable. Instability may appear blue screens death, freezes in programs. This behavior of the Windows operating system is caused by file system errors. In this case, it will help us console command « chkdsk". By running the "chkdsk" command, you can fully restore functionality Windows OS. For this example, we will take a computer with a new operating system. Windows system 10. First of all, let's open the console in Windows 10 as an administrator. This can be easily done by clicking right click mouse icon " Start” and selecting the item we need.

In the running console, execute the following command CHKDSK F: / F / R After checking with command application"chkdsk" in the console will display the result of the check.
Now consider the command " CHKDSK F: /F /R» more. Immediately after the "chkdsk" command comes the letter " F"- this letter local disk where we correct errors. Keys " /F" and " /R» fix errors in the file system, as well as fix bad sectors. These keys are used almost always, unlike the others. You can view the rest of the keys with the chkdsk /?
It is also worth noting that in Windows 10, the capabilities of the “chkdsk” application have been significantly expanded thanks to new keys.
How to test a hard drive for health using DST
Abbreviation DST stands for Disk Self Test, that is self-test disk. Manufacturers specifically build this method into the HDD, so that later, using special software, they can perform DST self-diagnosis, which will identify problems. By testing the “screw” using DST, you can get data on probable breakdown winchester. It is especially convenient to use DST on servers and enterprise computers where secure storage information plays a big role. Now consider the use of DST on the example of HP laptops. For new HP notebooks with support UEFI BIOS there is a special diagnostic menu " Startup Menu". is running this menu by using power key and key combinations ESC.

To run system tests, press the F2 button.

In the window that appears, DST is called Hard Disk Test. After selecting it, a self-test will start.

Other manufacturers also have a DST method, only running on a PC from other manufacturers is different from the above.
Checking a hard drive in Linux
For example, let's take a computer based on the Ubuntu 16.04 operating system. To do this, launch the terminal in Ubuntu. In the terminal, type the following command sudo apt-get install smartmontools This command should install
If you don't like working in console mode, you can install a graphical utility gnome-disk-utility. In it you can see everything you need about the HDD and its status.

Summing up
In the reviewed article, we described how you can monitor the status of the HDD, as well as how to fix its sectors and file system, if possible. From the material it becomes clear that monitoring the status of hard drives is very important, as it allows predict HDD failure.
If you find that your hard drive is problematic, then do not postpone its replacement for later. A problematic "screw" can fail at any time, and you will lose all the information stored on your computer.
We hope that our material will be useful to our readers, and will fully help to solve the problem. hard checks disk.
Related videos
