Some time ago, IrDA or infrared was well known to most advanced users of mobile devices. But, then the popularity of this technology fell significantly and almost everyone forgot about it.
Now IrDA is gradually returning to phones, smartphones and other mobile equipment. Therefore, it would not be superfluous to recall what IrDA is, and also to tell why an infrared port is needed in modern devices.
The abbreviation IrDA stands for InfraRed Data Association and stands for infrared (IR). An infrared port is an optical communication line that uses the infrared range of light waves to transmit data. Infrared was most popular in the late 90s and early 2000s. Now, the use of IrDA has practically been abandoned, replacing it with such modern wireless technologies like wifi and bluetooth. The reason for the rejection of infrared data transmission was a lot of shortcomings. For example:
- The use of IrDA complicates the design of the device case, since for the operation of the infrared port in the device case it is necessary to provide a transparent window.
- Usage optical line communication imposes severe restrictions. IrDA requires the receiver and transmitter to be in line of sight. The transmission range is also limited.
- The first IrDA standards did not provide the required data transfer rate.
At the time of the popularity of IrDA, it was used in a wide variety of techniques. In particular, infrared could be found in most mobile phones, pocket computers and laptops. Also often IrDA was used in printers, scanners and digital cameras. Thanks to IrDA, all these devices could communicate by transmitting light signals in the infrared range.
But, IrDA is no longer used for data transmission, as now there are more convenient solutions for this. The only area where the infrared port is still used is the remote control of equipment. For example, remote controls for TVs, players, air conditioners use the infrared port.
Why IrDA in a modern phone
Application for managing equipment on Samsung smartphone Note 4.
In modern mobile phones and smartphones, IrDA is used exclusively for remote control technique. With the help of infrared, the phone can be turned into Universal remote, which can be used to control TVs, multimedia systems, air conditioners and other equipment.
You will need a special application to control equipment using the infrared port. Usually such an application is already on the list. standard applications set by the device manufacturer. But, if you wish, you can use applications from third-party developers. AT Google Play Market has many applications that allow you to control equipment using infrared. For example, you can use applications such as:, or.
It is very easy to work with these applications. You need to specify the model of the device that you want to control, after which the buttons will appear on the screen, as on a conventional remote control. Then direct the phone's infrared port to the device and press the buttons in the application.
What is the infrared port for? Such a device allows you to create a stable connection between the computer and other devices (equipped with infrared ports) without the use of wires. For example, it could be a scanner or a printer. Although now most users purchase such a device for communication desktop computer with a pocket computer or, more often, a cell phone. The last two devices have a fairly primitive input system and, of course, its expansion increases the comfort of working with information. The mobile phone has become an affordable device for most computer users. Infrared, which is equipped with many phone models, allows you to edit content notebook device through an ordinary computer. You can easily change the logo on the display or set a ringtone. A rather interesting function that appears in the owner of a mobile device is network monitoring, which will provide the most comprehensive information on the network. It is impossible not to say about such a service of almost all cellular operators as mobile Internet. In this case, you can access the World Wide Web through your mobile phone. In other words, you become Internet users at any point where the operator you need works. This is quite expensive, but in some cases there are no alternatives to solve this problem. Let's take a closer look at this wonderful device.
Types of IR ports (by connection):
Devices of the second and third types are universal. In other words, if you buy such an IR transceiver, it will fit on your computer without any complications. If you liked the IR port that connects to the IrDA motherboard connector, then problems may arise. Read the instructions carefully and consult with the seller. For example, the ASUS infrared port only works on motherboard the same manufacturer. Very convenient infrared ports are made by one of the Chinese companies (there is no manufacturer's name on the plastic bag). The connector for connecting to IrDA is made according to the “assemble me yourself” principle. On the one hand, it clearly lacks mechanical strength, and it is very difficult to insert it into the motherboard connector. But on the other hand, you can easily, without resorting to the help of a soldering iron and tweezers, assemble the desired connector, thereby ensuring the necessary "pin" compatibility. This flexibility of the solution makes it very attractive to buy. Although the quality of Chinese IR ports... Let's not talk about bad things. In the future, we will talk about the characteristics of such devices.
Working conditions
IR communication devices can not be called very capricious, but still you need to talk a little about the conditions for their operation. First of all, you should know that the wavelength of infrared ports is in the range from 850 to 900 nm. Most often, this value is 880 nm. So organizing strong interference is a fairly simple matter. Let's start with examples:
- The windows of the apartment, located on the fifth floor, face the western side. Toward evening, the IR receiver / transmitter stopped seeing cellular telephone equipped with such a system. This bundle was on the table and was not covered by anything. The cause of the interference was found without any problems. The bright spring sun was to blame for everything. Avoid direct sunlight when using IR devices.
- In the evening, when the fluorescent lamp was turned on, the situation repeated itself. However, it is worth noting that the connection was still there, but very often broke off. The fluorescent lamp must be covered or turned off during the operation of IR devices.
- The TV, which is located in close proximity to the desktop, is equipped with a remote control. When switching channels or any other manipulations with the "sloth" working programm regularly issued a message that an extraneous IR device was working in direct proximity and demanded to turn it off. Whether this interfered with data transfer or not is unknown, but until the remote control was removed (you can read “it was turned off”), nothing could be done with the program. When working with an IR device, remove any extraneous IR transmitters in the area of the IR port.
Exclude all sources of IR waves in the range of 850-900 nm from the line of sight of the IR receiver. Reflected waves can bring problems, but to a lesser extent. In a word, all interference cannot be foreseen, but it is always possible to remove their cause. The working distance between two IR devices should not exceed one meter. Otherwise, the system will be unstable. The directivity diagram of the infrared port, which is indicated in the instructions for it, to put it mildly, does not stand up to criticism. Try to place the devices directly opposite each other. Foreign objects placed between the infrared port and the working device will not contribute to better job. There were cases when they tried to connect a cell phone in a case via infrared to a computer. Nothing worked until the translucent cover was removed.
Connection
Connect infrared to personal computer simple enough. But in any case, it is recommended to spend ten minutes carefully studying the instructions for the device. Even if you do not learn anything new from it, you will feel confident during the installation.
Hardware
Connect the infrared port to the COM port connector. Remember the COM port number - this will be useful to you later. When connecting the IR port to the IrDA connector of the motherboard, unscrew the case of your system block and, having read the description of your motherboard, insert the connector (four-pin ruler) into the desired socket. The first wire is marked on the board with the number 1 or is indicated in the description of the motherboard. The first wire of the IR connector has a color mark. Pull out the rear plug free place and you can assemble the body. Connect the pigtail connector with the IR receiver/transmitter to the socket on the cap. The jack and connector are very similar to the PS/2 connector.
Software part
Here is a description of the setting software for the operating system MS Windows 98. For other operating systems from Microsoft, it is similar. It is possible to connect the infrared port to computers with other operating systems, but the description of the infrared port says: “Designed to work with operating systems Windows systems 95 and above. Experiment, maybe you will succeed.
When you set the IR port to COM, you are in for a happy voyage. Included with the device is a CD-ROM, installing drivers from which will not be difficult. Correctly set the port number to which the IR port is connected. See if the COM port is being used by another device, such as an internal modem. Also check BIOS settings for a parallel port, it must be set to ECP mode, not Normal or SPP (the default).
When installing an internal infrared port, it is worth doing a little more manipulation with your hands. First of all, enter the BIOS and enable the second COM port. Typically, below is the option to enable IrDA. Activate it. Next, establish a half-duplex link. If your BIOS contains other settings, then set them to the "default" mode. There will be problems - read the instructions and experiment with the settings. You cannot bring harm or physical damage to your computer.
Download operating system. If you did everything correctly, then the new device will be detected by the system itself. Next, you will be prompted to select the type of device. To be safe, do it manually. Select "IR DEVICES" and then the standard device type. Set the virtual port and remember its number. You will need it to configure most programs. The menu "Properties: System" will acquire one more item - "Infrared Communication Devices".
Reload the machine.
After that, an icon in the form of a flashing light bulb will appear in the lower right corner.
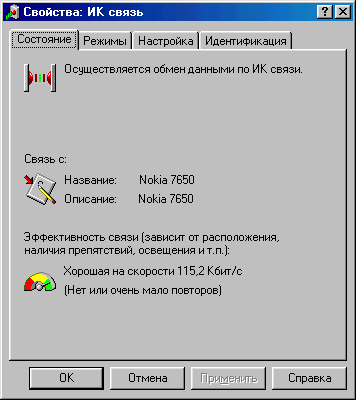
When you open it, you will see the IR communication properties.

Among all the settings, it is worth highlighting only “Modes”. Here you can enable IR communication and set the time after which the IR port will search for IR devices in the line of sight. You can disable the "Limit baud rate to:" option.
Now, if you place another activated IR device within the range of your IR port, you will hear a sound and see something like this on the screen:

That's it, your infrared port is fully configured, now you can use it. For example, send a picture from your phone to your computer. Next, we suggest you look at the most fashionable and popular application of the infrared port device in conjunction with a mobile phone - Mobile Internet.
Mobile Internet
Most Operators cellular network operating in the GSM-900/1800 standard offer such a service as "Mobile Internet". What it is? With a cell phone equipped with an IR receiver/transmitter and a modem, you can access the world wide web and use it as with a normal dial-up connection. The advantages of such an entrance to the network are obvious. First of all, you untie yourself from annoying telephone wires and become mobile (if you use a laptop). But the network through a mobile phone has its drawbacks. We recommend that you find out in advance how much (in monetary terms) such entertainment will cost you. The second disadvantage is the speed of mobile Internet. It is 9600 bps and no more. With the introduction of new technologies, this figure may soon increase. Setting up mobile Internet does not take much time. Here is your procedure. Make sure your cell phone is equipped with an infrared port and a modem. Turn on the infrared port on your mobile phone. After that, place it within the range of the infrared port connected to the computer (about 1 m).
Now you need to configure the modem built into the phone. To do this, you need to enter the "Settings" menu, then "Modem" and manually install the "standard 19200 modem" (if you have a special driver for your cellular modem, then put it). When installing, do not forget to specify the correct virtual port that was created when connecting the infrared port to your computer. Everything, the modem setup is finished. Reboot the system. To establish a connection, you need to create a "New Connection" (you can find out the parameters for it from your mobile operator). Internet via cell phone is at your disposal. Mobile Internet is quite an important and interesting addition to your computer.
Instead of a conclusion
The infrared communication between the computer and other devices is relatively short distance. However, its capabilities are widely used among mobile technology. Most likely, in the near future, infrared communication will give way to more advanced types of communication (for example, Bluetooth - several tens of meters). But so far, none of the motherboard manufacturers have abandoned IrDA, and you can buy an infrared port with peace of mind. Although before you make a purchase, make sure that your phone and computer can transmit data in the infrared range. We hope that after reading this article, you will be able to select and enable the infrared port without any problems.
Hardware implementation
The hardware implementation, as a rule, is a pair of a transmitter, in the form of an LED, and a receiver, in the form of a photodiode, located on each side of the communication line. The presence of both a transmitter and a receiver on each side is necessary for the use of guaranteed data delivery protocols.
In some cases, such as when used in remote controls household appliances, one of the parties can be equipped only with a transmitter and the other with a receiver only.
Sometimes devices are equipped with several receivers, which allows you to simultaneously communicate with several devices. The use of a single transmitter is possible due to the fact that logical layer protocols require only a small return traffic to ensure guaranteed data delivery.
Having multiple transmitters is much less common.
Most optical sensors used in photo and video cameras have a sensitivity range much wider than the visible part of the spectrum. Due to this, a working infrared transmitter can be seen on the screen or photograph as a bright spot.
Capabilities
AT Everyday life we constantly encounter IR ports every day.
The remote control sends commands to the TV or VCR using IrDA. Now IR ports are still equipped with most mobile phones, laptops and PDAs. Some printers and digital cameras are equipped with infrared ports. Most desktop PCs, on the other hand, do not have an infrared port in the standard system configuration, and they require an IR adapter that connects to the computer via a COM port or to a special connector on the motherboard.
Via infrared, protocol high level- IrOBEX can, for example, send a mobile phone or a computer that also has an infrared port. The same protocol allows you to organize data synchronization.
The IrCOMM protocol allows a mobile phone to be used as a wireless modem.
The IrLAN protocol allows you to connect devices to a local network, like software.
IrPHY
IrPHY (Infrared Physical Layer Specification)- represents the lowest level mandatory protocol among the IrDA specifications. Corresponds to the physical layer of the OSI network model
The main characteristics of the IrPHY specification are as follows:
- Range: at least one meter. HAMID
- Minimum supported deviation from the axis of the receiver/transmitter: not less than 15°.
- Data transfer rate: from 2.4 kbps to 16 Mbps (100 Mbps version is under development).
- Modulation: unmodulated signal, no carrier.
- Wavelength: 850 to 880 nanometers.
- Data transfer mode: half duplex.
Interestingly, the specification does not define the maximum allowed values for such parameters as distance or deviation from the axis, however, the typical location of devices for organizing the connection implies a distance of 5 to 50 centimeters, on the same axis. Devices with one-way communication (such as a remote control and a TV) typically support a range of at least 10 meters.
The use of the half-duplex mode is motivated by the fact that, when trying to simultaneously receive and transmit data, the radiation of your own transmitter will greatly interfere with the reception of a signal from the remote transmitter, which makes the implementation of the full-duplex mode very difficult and impractical.
Data rates are divided into several subranges - SIR, MIR, FIR, VFIR, UFIR, each of which is characterized not only different speeds but also using different code schemes. Which, in fact, makes faster data transfer possible.
SIR
"Serial Infrared (SIR) uses the same baud rates as found in the RS232 serial connection specification (COM port), namely 9.6 kbps, 19.2 kbps, 38.4 kbps, 57.6 kbps, 115.2 kbps. The coincidence of supported speeds is not accidental, and makes it quite easy to implement COM IrDA adapters.
As a rule, the lowest available speed for devices is exactly 9600 bps and it is this that is used to transmit search, alert and pairing signals.
MIR
MIR - Medium Infrared- Supports data rates of 0.576 Mbps and 1.152 Mbps.
Although MIR is not an official term for IrDA, the fact that the coding scheme used for these rates is different from both SIR and FIR makes this term quite convenient and common.
FIR
Fast Infrared- an obsolete IrDA specification term previously used to refer to devices supporting data rates from 9600 bps to 4 Mbps, which includes both SIR and MIR.
Nowadays, as a rule, the term FIR is used to refer to the actual speed of 4 Mbps.
Some sources use the term FIR to refer to all speeds above SIR.
VFIR
Very Fast Infrared is a term used to denote support for transmission rates up to 16 Mbps.
While specification details are still under development, this moment, 16 Mbps is the most high speed data transmission over IrDA supported by serial devices.
For example, the TFDU8108 infrared transmitter supports all data rates from 9.6 kbps to 16 Mbps.
UFIR
Ultra Fast Infrared- is under development, expected to support speeds up to 100 Mbps.
IrLAP
Infrared Link Access Protocol - a mandatory second-layer protocol, located on top of IrPHY, corresponds to the link layer of the OSI network model.
IrLAP is responsible for:
- Access control.
- Search for nearby devices.
- Establishing and maintaining a bidirectional connection.
- Distribution of primary and secondary roles among devices.
IrLAP divides all communicating devices into one Primary and the rest (one or more) Secondaries. The Primary device controls all Secondaries and can transmit data to them without "permission". The Secondary device can only send data upon request from the Primary.
IrLMP
Infrared Link Management Protocol- obligatory protocol of the third level. Corresponds to the network layer of the OSI network model.
Consists of two sublevels - LM-MUX (Link Management Multiplexer) and LM-IAS (Link Management Information Access Service).
LM-MUX is responsible for:
- separation of the data stream into different communication channels.
- change of Primary/Secondary devices.
LM-IAS is responsible for:
- publishing a list of available services.
- access of client devices to published services.
IrCOMM
Tiny TP
IrOBEX
IrLAN
IrSimple
IrFM
Other short range wireless interfaces
- Wibree
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010 .
- Chirchik (river)
- Cent (disambiguation)
Technical Translator's Handbook
infrared interface- Interface used for wireless connection devices (printer, mouse, keyboard, etc.) that have an infrared port. Topics Information Technology in general EN infrared interface … Technical Translator's Handbook
IR port- External IR port in the Siemens CXT70 IrDA Infrared Data Association, IR port, Infrared port is a group of standards that describes the protocols for the physical and logical level of data transfer using the infrared range of light waves in ... Wikipedia
IR port- External IR port in the Siemens CXT70 IrDA Infrared Data Association, IR port, Infrared port is a group of standards that describes the protocols for the physical and logical level of data transfer using the infrared range of light waves in ... Wikipedia Wikipedia
From the article you will learn
Android smartphones have many useful features. In addition to supporting the 2G, 3G modules required for communication, Internet LTE and other things, they are equipped with light sensors, proximity, accelerometer, and some even have an infrared port. It is about such smartphones that will be discussed in this article. Let's figure out what an infrared port is and how it will help turn your mobile into a TV remote control. You will find out which devices support this feature.
What is an infrared port?
An infrared or infrared port is a special indicator on a smartphone using the infrared range of light waves as a transmission medium. It is he who is used in all remotes for TVs.
Simply put, an infrared port is a simple light bulb on a remote control or a smartphone that sends rays to a TV, which receives them, decrypts and understands the command set in this way.
Some Android smartphones have an infrared port and can be used as a remote control, which is quite convenient.
How to determine that the smartphone has an infrared port?
It is very strange, but most manufacturers refuse the infrared port, they say, this is already an old technology. The main manufacturers installing the infrared port today are Xiaomi and Huawei.
As a rule, an infrared port is present in most phone models of these companies. In general, there has been such a trend that in almost all Chinese smartphones there is an infrared port.
Checking for an infrared port is very easy. It looks like a red light bulb on the top of the smartphone. Approximately like this:
You can also go to the characteristics of your mobile device and see if it has an infrared port to control household appliances.
What equipment can be controlled?
Unfortunately, mobile phone manufacturers put a "cropped version" of the infrared port to reduce its size. Therefore, it is possible only to send an infrared beam, but not to receive it.
It turns out that the infrared port can be used to control home appliances. But there is one important condition here: the remote control with which you control the equipment must be supported by a special application on your smartphone. Thus, purely theoretically, you can control any technique, but in practice, control requires the support of a remote control. To find out if this remote control is in the database of a special application, you just need to try to find the brand of your equipment and try to establish contact, which is discussed below in the article.
The smartphone can be used to control the following types of equipment:
- Television;
- TV set-top box, tuner, DVD;
- Projector;
- Air conditioner;
- Mi TV, Mi Box;
- Fan;
- AV receiver;
- Camera.
How to make your phone a remote control for home appliances?
In order to make a remote control from your smartphone to any device in the house, be it a TV or an air conditioner, you need to perform a couple of simple steps, namely:
As already mentioned, to control household appliances from an Android phone, we need a special application. In this article, we will use a proprietary application from Xiaomi - Mi Remote. But you can use any other. All of them are very similar in their functionality and if you figure out how to use Mi Remote, you will understand how others work.
You can download the app from the official app store from Google entitled Play market(or Google Play) completely free.
The application is distributed without paid subscriptions and without ads, because this is the official software for owners of MIUI firmware in smartphones from Xiaomi. But anyone can install it, even if you have a device from another manufacturer and do not have an infrared port.

Step 2 — Setting up Mi Remote
After the first launch of the program, we need to add our first remote control. To do this, click the "Add" button or on the plus sign at the top right:

Pay attention to the fact that in some similar applications this item may be slightly different. For example, the item "Tuners" may be present, but there will be no "DVD player", and so on. Therefore, if the equipment you need is not available, just download a similar application. Some of them will be listed at the end of the article.

Then, when we have chosen the type of equipment, we are looking for a brand. There are a lot of brands, so we recommend using the search. If suddenly you have very few brands, then just connect to the high-speed WiFi networks and they themselves will be loaded from the cloud.

The last step in the setup is a health check. The system will prompt you to press the button by directing the infrared port of the smartphone towards the equipment. If the equipment receives the signal and performs the appropriate action, it means that you have chosen everything correctly and now you can fully use your smartphone to control home appliances.
In the event of a malfunction, you can either choose a different brand or try other button options. Often, not all buttons in the remote will work, so we recommend experimenting a little. Also try to change the brand, since the remote control signed in the application as this brand is not always suitable for this or that technique. For example, remote controls from Weston and Walson fit an old West TV. Strange, but they both work.


Step 3 - Using the Mi Remote App
After successful setup, you can start using the application.
To open the remote control menu, just launch this application and select the appropriate technique that you previously set as default in the application. On the main screen, you can add an infinite number types and brands of equipment.
Easy to manage:
- Power button. Turns equipment on and off. In this case, TV.
- Change configuration button. With its help, you can change the control style: taps or swipes.
- The main working part of the console. Here are the main buttons like switching channels, changing the volume, and so on. It is this area that can be used as swipes if you change the setting in button 2. Instead of pressing up, you will swipe up, instead of pressing down, you will swipe down, and so on.

The application has support for working with several remotes at once. You can add an infinite number of different remotes and give them all any name.
In order to proceed to the selection of the required remote control or create a new one, go to main screen apps Mi Remote. To do this, either simply re-enter the application, or click on the "Back" arrow at the top right. You will be taken to the main screen. It is extremely simple. At the top right there is a plus sign already familiar to us from the first addition of the remote control, it makes it possible to add a new remote control.
The concept of an infrared port at first practically disappeared from the mobile world, and now it has appeared again.
Many are familiar with infrared for a long time and consider it a passed stage of technological progress. However, even such simple device have been used even today.
Why does a smartphone need an infrared port?
Now the infrared port (IrDA: Infrared Data Association) is used far from transmitting information, because it has been replaced by Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. A new purpose - remote control of all kinds of consumer electronics.
With the purchase of a smartphone equipped with an infrared port, a universal remote control falls into the hands of the user. With it, you can switch the TV channel with a couple of touches of the display, adjust the temperature of the air conditioner, start the coffee maker, and so on. This feature will allow you to throw out a bunch of bulky remotes and forget about the constant purchase of batteries.
Applications for the infrared port of a smartphone
Buying a gadget equipped with an infrared port is only half the battle. Next, you need to install one of special applications, which are enough on Google Play. We will consider the most convenient of them.

Control it is not one universal remote control, but a whole set. You download the necessary remote controls from the database and use them alternately. The data warehouse is constantly updated and supplemented with new remote controls.
There are both paid and free version applications. However, only 3 remotes can be used for free at the same time while watching the ubiquitous ads.
Galaxy Universal Remote is a paid app that justifies its price. It will allow you to manage multiple devices: from regular TV to a robotic vacuum cleaner. All saved settings can be placed as a widget on the smartphone's desktop, which saves you a lot of time. Nice design and no intrusive ads.
The list is completed by the ZaZaRemote application, which is very difficult to compete with. ZaZaRemote supports more than 6 thousand devices and has a database of 250 thousand remote controls for every taste. The application offers a minimalist design and the function of grouping appliances by room.
Alternative
If you want to test this technology, but you do not want to buy a smartphone with an infrared port, there is an alternative. Just buy an infrared transmitter (TV dongle) for the right device. There are many of these devices, the cost varies between 200-500 rubles.
Infrared (IrDA) on your smartphone can make life a lot easier - control your home appliances, TVs and other home devices with it.

